Interventional Radiology
What is Interventional Radiology?
Interventional Radiology, also known as IR, is a subspecialty of radiology focused on performing therapeutic and diagnostic procedures through tiny incisions or catheters. The procedures are guided by real-time imaging, such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds, allowing interventional radiologists to precisely target and treat various conditions, including vascular diseases, cancers, and organ abnormalities.
Interventional radiologists complete extensive medical training, first becoming certified in diagnostic radiology and then completing an additional 1-2 years of fellowship training in interventional techniques. This specialized expertise allows them to accurately interpret images and safely navigate instruments through the body's pathways to reach target sites.
If you have symptoms or conditions that may benefit from targeted, minimally invasive approaches, seeing an interventional radiologist can open up effective treatment options while reducing pain, recovery time, and complications.
When to See an Interventional Radiologist
If you have been diagnosed with certain medical conditions that require invasive treatment, and minimally invasive image-guided treatment is a treatment option, your treating physician may recommend you see an interventional radiologist. Their expertise in precisely targeting invasive treatments through small incisions or catheters can provide effective solutions while avoiding open surgery.
Seeking evaluation and treatment from an interventional radiologist at the initial onset of symptoms or shortly following diagnosis is key. Early intervention can optimize outcomes for many disorders.
Here are some specific instances when you should consider an interventional radiologist:
- Blood Vessel Blockages
If you have arterial blockages or narrowing causing poor circulation, an interventional radiologist can open the blood vessels through angioplasty and stenting. - Spinal Fractures
For vertebral compression fractures, kyphoplasty can repair and stabilize the bone while reducing pain. - Blood Clots
Insertion of IVC filters by interventional radiologists prevents clots from reaching the lungs. - Tumors
Image-guided biopsies, ablations, and treatments like chemoembolization can target tumors with minimal invasiveness. - Infections
Interventional radiologists can drain abscesses, inject antibiotics, and treat infections without open surgery. - Dialysis Access
Maintaining and repairing fistulas/grafts or placing dialysis catheters is done by interventional radiologists. - Aneurysms
Minimally invasive coil embolization and stent graft procedures can treat aneurysms through a small puncture.
Interventional Radiology Diagnostic Tests
Interventional radiologists utilize a broad spectrum of imaging tests to accurately visualize medical conditions and guide targeted treatments. These minimally invasive diagnostic procedures provide detailed views of anatomy and function without surgery.
Precise diagnostics are integral for interventional radiologists to deliver personalized therapies tailored to each patient's specific needs. Pinpointing the location, morphology, and extent of an issue allows them to plan the most suitable image-guided intervention.
Some key diagnostic modalities used in interventional radiology include:
- CT Angiography
Provides images of blood vessels and organs by using contrast dye. Useful for visualizing vascular blockages, aneurysms, tumors, and other abnormalities. - MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging produces detailed 3D images of soft tissue structures. Helps identify and characterize tumors, spinal issues, joint problems, and more. - Ultrasound
Uses sound waves to obtain real-time images of anatomy and blood flow. Guides vascular access and interventions. - Fluoroscopy
X-ray imaging that visualizes internal structures in motion during procedures. Enables precise navigation and device positioning. - Digital Subtraction Angiography
Contrast dye is injected to highlight blood vessels on an x-ray. Evaluates aneurysms, blockages, bleeding, and anatomy. - Fistulogram
An x-ray test that evaluates dialysis fistulas and grafts to guide interventions improving blood flow. - Discogram
Contrast dye is injected into spinal discs to assess disc integrity and pinpoint sources of back pain.
Interventional Radiology Procedures and Treatment Options
Interventional radiology offers a wide range of specialized procedures that use real-time image guidance to treat various medical conditions with minimally invasive techniques. These targeted procedures provide patients with effective treatment options and faster recovery times compared to open surgery.
Some common interventional radiology procedures and their treatment applications include:
- Angioplasty & Stenting
This procedure is used to treat narrowed or blocked blood vessels (arteries or veins). During angioplasty, a small balloon is inflated inside the narrowed vessel, widening it to improve blood flow. Stents, tiny mesh tubes, may be inserted to keep the vessel open and prevent future blockages. - Kyphoplasty
Kyphoplasty is a procedure used to treat spinal fractures caused by osteoporosis or trauma. It involves injecting bone cement into the fractured vertebrae to stabilize the spine and relieve pain. - Hemodialysis Fistula Maintenance
For patients on hemodialysis, maintaining a properly functioning fistula is crucial. Interventional radiologists can perform procedures to clear blockages and ensure optimal blood flow for successful dialysis treatment. - Port Placement/Removal
Ports are implanted devices used for chemotherapy or long-term medication delivery. Interventional radiologists can place or remove these ports with precision, offering patients a convenient and safe treatment option. - IVC Filter Placement/Removal
IVC (inferior vena cava) filters are used to prevent blood clots from reaching the lungs. Interventional radiologists can place or remove these filters when necessary to protect patients from pulmonary embolism. - Permcaths
Permcaths are long-term vascular access devices used for medical treatments like dialysis or chemotherapy. Interventional radiologists can insert and manage these catheters, ensuring proper functionality. - Tumor Ablation
Ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency or microwave ablation, are used to treat certain tumors, including liver, kidney, and lung tumors. The targeted tumor tissue is destroyed using energy delivered through a needle-like probe. - Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
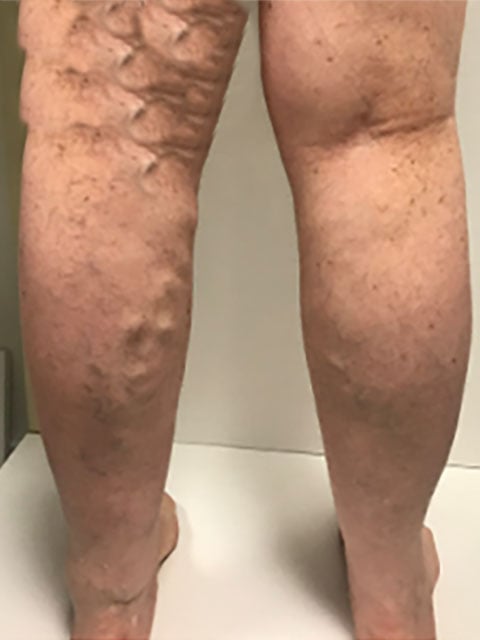
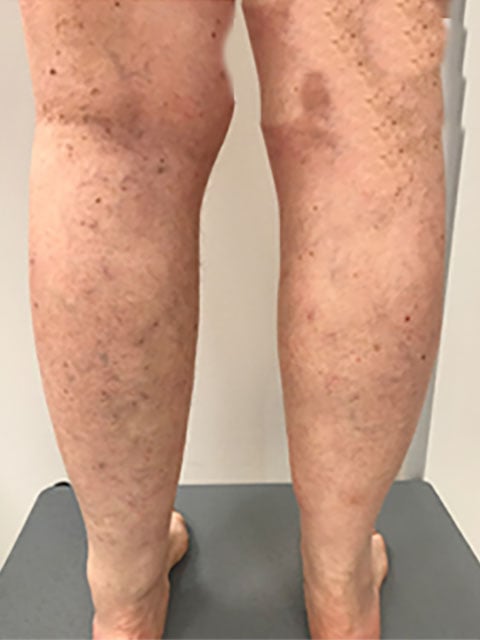
UFE is a non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids. It involves blocking the blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink and alleviating symptoms. - Varicose Vein Treatment
Minimally invasive procedures like endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) or sclerotherapy can effectively treat varicose veins, improving blood flow and reducing symptoms.
Photo Gallery
Video Gallery
Testimonials
Dr. Mathias is a good communicator and makes sure you understand his prognosis.
He thinks out loud. I literally have to trust him with my my life and it helps that he doesn’t rush your appointment.
He’s the best!
Dr Mathias is not only very knowledgeable and the best in cardiac catheterizations that are challenging, but he remembers every detail of my cardiac history and managed my post-Takotsubo event wonderfully! He listens and will answer all questions with research studies and teach.Dr. Massey is a very good Cardiologist.
Dr. Massey is a very good Cardiologist, has years of experience and very caring. I have no problem with the clinic.Wonderful, kind, and compassionate.
Very polite. Dr. Kumar is thorough. Genuinely concerned about his patient. Reviews all information and answers questions. Wonderful, kind, and compassionate. Highly recommend.I feel confident about the care he provides to me.
Dr. Kim is so good at explaining test results and how it impacts my condition. He explains changes in medication and spends time teaching about my heart condition, medications and signs to look out. I feel confident about the care he provides to me.
I’m very appreciative of having CVA on my side.
Dr. Thomas Kim has been cardiac guardian since day one, back maybe 10 years. He takes as much time as needed, and I’m an active participant of my treatment. I send him messages through portal and get taken care of promptly. The office doesn’t always manage coordination effectively, but it’s not the physicians. My visits don’t take more than 30 min.The doctor was thorough and knowledgeable.
This office was well organized, equipped, and ready for the visiting patients.
Everyone was polite and helpful.
The doctor was very helpful, the doctor read each of my results and made sure I understood.
Photo Gallery
Interventional Radiologist Near Me
In Search of Care? Request a Consultation Today